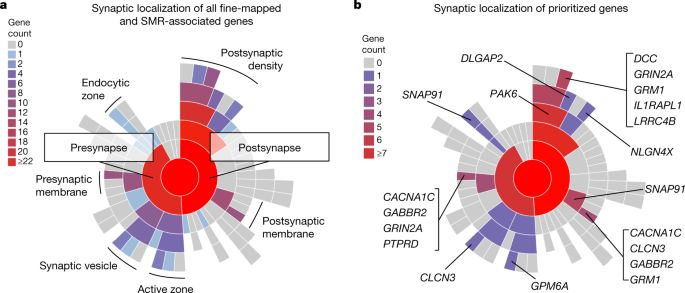
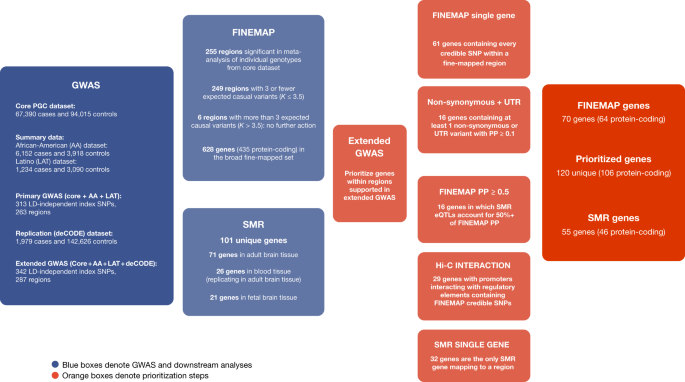
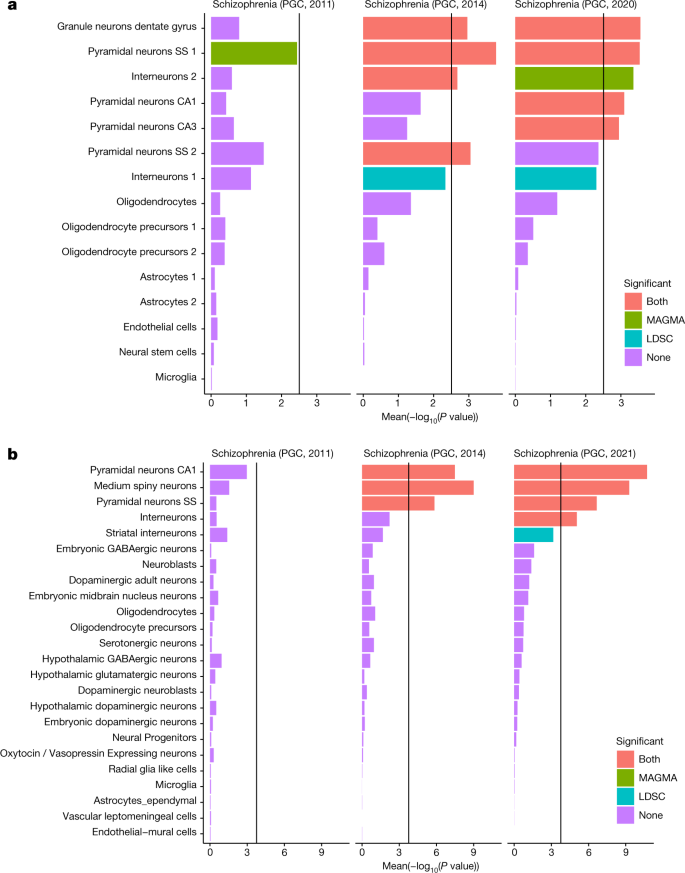
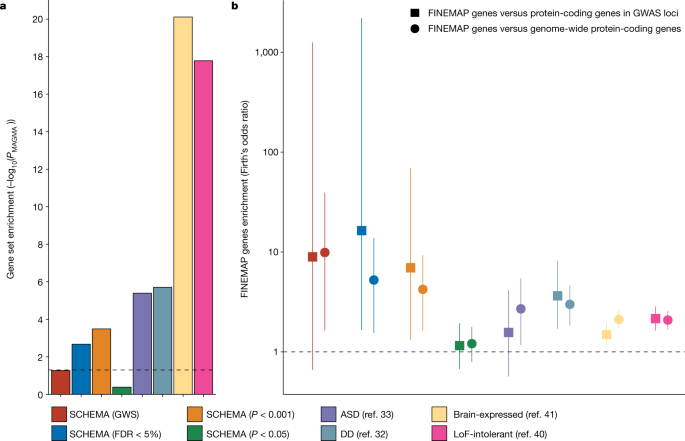
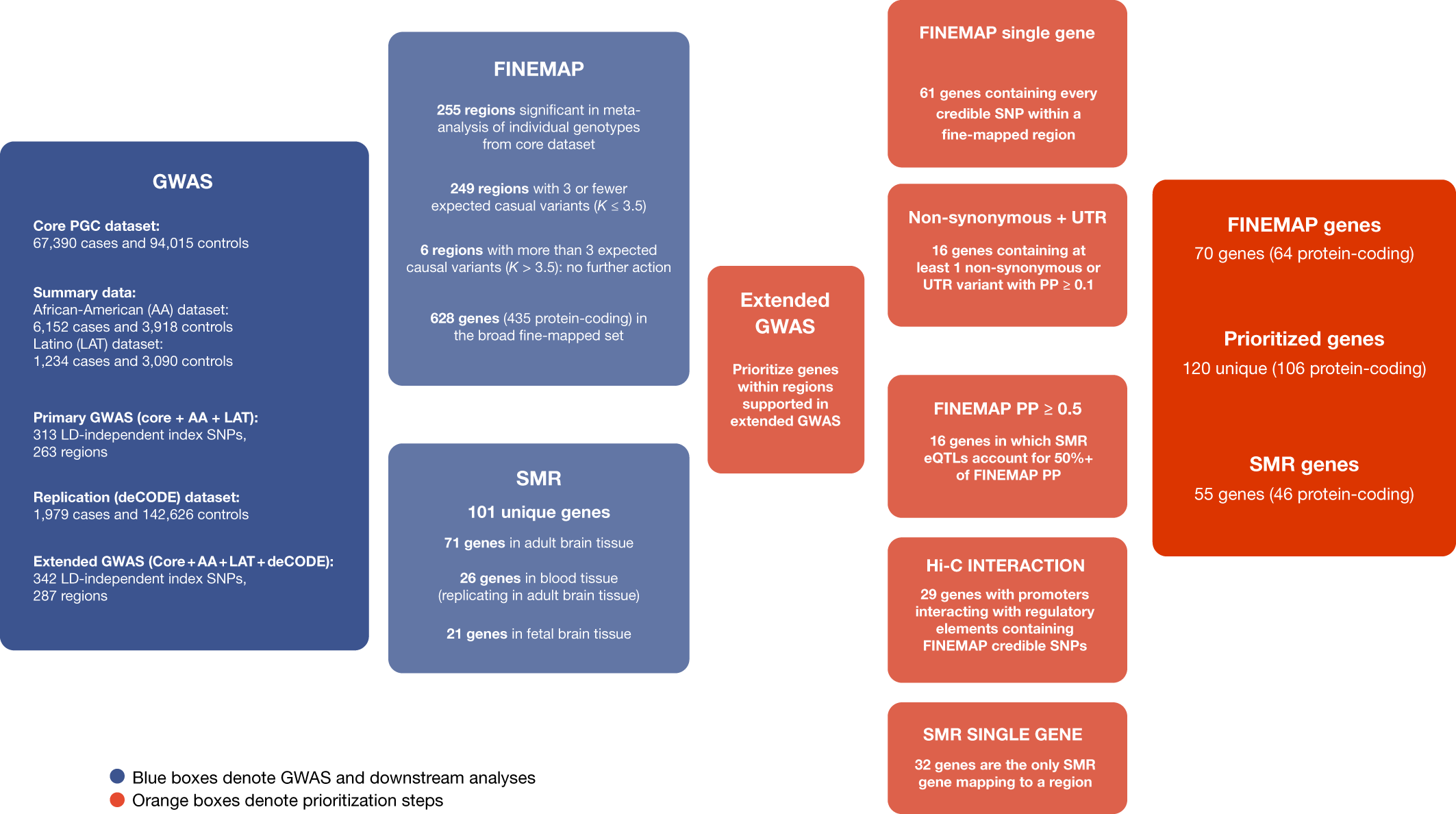
Mapping Genomic Loci Implicates Genes And Synaptic Biology In Schizophrenia – Genome-wide association studies have shown that variants Conclusion These data highlight the usefulness of mapping disease susceptibility loci using a transancestral approach, particularly in a . The biocuration effort to analyze the multigenic, highly conserved IG and TR gene families is of paramount importance Additionally, comparative genomics studies of the IG and TR loci are .
Mapping Genomic Loci Implicates Genes And Synaptic Biology In Schizophrenia
Source : www.nature.com
Mapping genomic loci prioritises genes and implicates synaptic
Source : www.medrxiv.org
Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in
Source : www.nature.com
Using brain cell type specific protein interactomes to interpret
Source : www.cell.com
Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in
Source : www.nature.com
Advances in our understanding of the genetic contributions to
Source : www.ucl.ac.uk
Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in
Source : www.nature.com
Mapping genomic loci prioritises genes and implicates synaptic
Source : www.medrxiv.org
Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in
Source : www.nature.com
Mapping genomic loci prioritises genes and implicates synaptic
Source : www.medrxiv.org
Mapping Genomic Loci Implicates Genes And Synaptic Biology In Schizophrenia Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in : Univariate heritability was estimated for each genomic block across SNPs in-common between a pair of traits, and only loci with local interpretation of fine-mapping and colocalisation results, . Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the schizophrenia risk as a function of long-term air pollution exposure presented as a time-varying variable. We also derived the schizophrenia .